Penelitian Unggulan
Terdapat beberapa tema penelitian unggulan dari setiap Kelompok Keahlian yang ada di Fakultas Informatika :
1. Penelitian Unggulan Kelompok Keahlian Data Science

DEVELOPMENT OF HYBRID SAMPLING TO IMPROVE THE PERFORMANCE OF CLASSIFICATION RESULTS ON UNBALANCED DATA
This study aims to develop a hybrid sampling method (a combination of oversampling and undersampling) to obtain better and more consistent classification results, especially for minor classes with different imbalanced ratio (IR) conditions from various dataset domains.
Adiwijaya, Isman Kurniawan
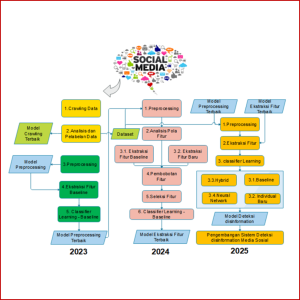
DETECTION AND ANALYSIS OF POLITICAL NEWS DISINFORMATION IN INDONESIAN SOCIAL MEDIA
In this research, we develop a disinformation news detection system using a machine learning approach that can distinguish between disinformation news and actual news. This system was designed to detect disinformation news on various Indonesian social media.
Yuliant Sibaroni, Sri Suryani, Aditya Firman
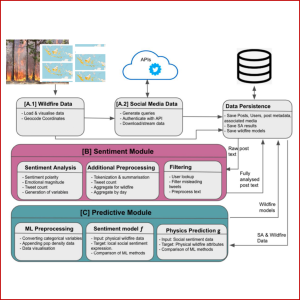
SOCIAL MEDIA MINING FOR DISASTER MANAGEMENT
This project constructs and builds a corpus dataset that may be utilized in a wildfire prediction model, employing social media data sources and sentiment analysis to forecast wildfire features. We also employ wildfire-specific variables to forecast online social dynamics, which have been demonstrated to indicate localized disaster severity. This work could be helpful for disaster management in detecting imminent hazard zones.
Warih Maharani, Prati Hutari Gani, Ramanti Dharayani.
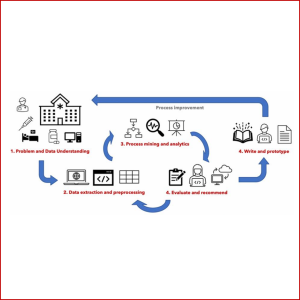
PROCESS MINING IN HEALTHCARE
In this study, we analyse BPJS Kesehatan sample data using process-oriented data science combining process mining and statistics. We treat healthcare treatments and diagnoses as healthcare processes; therefore, we can learn and analyse those processes to find patterns of the sequence of treatments and diagnoses.
Angelina Prima Kurniati, Gede Agung Ary Wisudiawan
2. Penelitian Unggulan Kelompok Keahlian Intelligent Systems
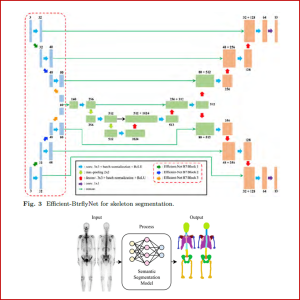
LEVERAGING MODEL SCALING AND BUTTERFLY NETWORK IN THE BONE SCAN IMAGE SEGMENTATION
As we all know, cancer is one of the leading causes of death world- wide and the second leading cause of death overall. This is why regular screenings or health checks are necessary to detect cancer lesions early. Since bone scan images have become the primary means of detecting the emergence of cancer lesions on bone, high segmentation accuracy is. essential for establishing the model of some predefined regions in bone scan images where cancer metastasis was predicted to appear. Con- sequently, robust. localization and identification of the specific region in bone scan images are required for automated metastasis detection. To this end, we propose Efficient-BtrflyNet, a new deep learning-based architecture for skeleton segmentation of whole-body bone scan images. The proposed architecture exploits the benefits of Efficient Net’s model scaling and the encoder-decoder design of butterfly-type networks. We added Efficient NetB7 to the encoder section to obtain more specific fea- tures. The proposed architecture simultaneously processes anterior and posterior whole-body bone scan images. Using 37 bone scan images, we evaluated the performance of our proposed skeleton segmentation system using the Dice score. Efficient-BtrflyNet achieves superior seg- mentation performance compared to the existing representative method.
Ema Rachmawati, Mahmud Dwi Sulistiyo, and Dimas Bayu Nugraha
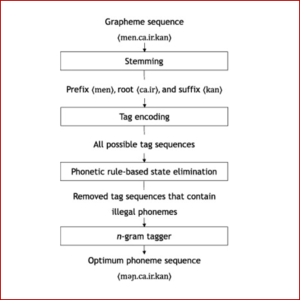
STEMMER AND PHONOTACTIC RULES TO IMPROVE N-GRAM TAGGER-BASED INDONESIAN PHONEMICIZATION
A phonemicization or grapheme-to-phoneme conversion (G2P) is a process of converting ga word into its pronunciation. It is one of the essential components in speech synthesis. speech recognition, and natural language processing. The deep learning (DL)-based state- of-the-art G2P model generally gives low phoneme error rate (PER) as well as word error rate (WER) for high-resource languages, such as English and European, but not for low- resource languages. Therefore, some conventional machine learning (ML)-based G2P models incorporated with specific linguistic knowledge are preferable for low-resource languages. However, these models are poor for several low-resource languages because of various issues. For instance, an Indonesian G2P model works well for roots but gives a high PER for derivatives. Most errors come from the ambiguities of some roots and derivative words containing four prefixes: (ber), (meng). (peng), and (ter). In this research, an Indonesian G2P model based on n-gram combined with stemmer and phonotactic rules (NGTSP) is proposed to solve those problems. An investigation based on 5-fold cross-validation, using 50k Indonesian words, informs that the proposed NGTSP gives a much lower PER of 0.78% than the state-of-the-art Transformer-based G2P model (1.14%). Besides, it also provides a much faster processing time.
Suyanto, Andi Sunyoto, Rezza Nafi Ismail, Ema Rachmawati, Warih Maharani
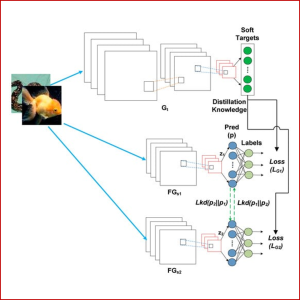
IMPROVING DEEP MUTUAL LEARNING VIA KNOWLEDGE DISTILLATION
Knowledge transfer has become very popular in recent years, and it is either based on a one-way transfer method used with knowledge distillation or based on a two-way knowledge transfer implemented by deep mutual learning, while both of them adopt a teacher-student paradigm. A one-way based method is more simple and compact because it only involves an untrained low-capacity student and a high-capacity teacher network in the knowledge transfer process. In contrast, a two-way based method requires more training costs because it involves two or more low-cost network capacities from scratch simultaneously to obtain better accuracy results for each network. In this paper, we propose two new approaches, namely full deep distillation mutual learning (FDDML) and half deep distillation mutual learning (HDDML), and improve convolutional neural network performance. These approaches work with three losses by using variations of existing network architectures, and the experiments have been conducted on three public benchmark datasets. We test our method on some existing KT task methods, showing its performance over related methods.
Achmad Lukman and Chuan-Kai Yang
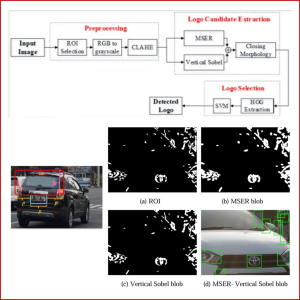
MSER-VERTICAL SOBEL FOR VEHICLE LOGO DETECTION
Detecting a vehicle logo is the first step before the actual recognition of the logo. However, detecting logos can pose difficulties due to various factors, including logo variations, differing scales andorientations, background interference, varying lighting conditions, and partial obstruction. This paper presents a vehiclelogo detection method using handcrafted features. We used a combination of Maximally Stable Extremal Region (MSER) andVertical Sobel. We combine vertical Sobel with MSER to overcome MSER’s limitation in recognizing objects of different sizes.These two features are merged using closing morphology operation to form blobs selected as logo candidate areas. Moreover, a Support Vector Machine (SVM) is implemented to choose alogo area by analyzing each candidate’s Histogram of Oriented Gradient (HOG). The proposed method was compared to other methods by implementing them on the samedataset. The significant advantage of using MSER-Vertical Sobel is its fast computation time. It is faster than other approaches that use non-handcrafted features. The test results show that the MSER Vertical Sobel can achieve high accuracy and the fastest computation time.
Gamma Kosala, Agus Harjoko, Sri Hartati
3. Penelitian Unggulan Kelompok Keahlian Cyber Physical Systems
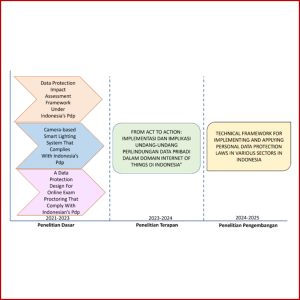
FROM ACT TO ACTION: IMPLEMENTASI DAN IMPLIKASI UNDANG-UNDANG PERLINDUNGAN DATA PRIBADI DALAM DOMAIN INTERNET OF THINGS DI INDONESIA
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa implementasi UndangUndang Perlindungan Data Pribadi dalam domain IoT di Indonesia masih dalam tahap awal, dan terdapat tantangan yang signifikan dalam memastikan perlindungan data pribadi. Penelitian ini menyimpulkan bahwa diperlukan penelitian dan pengembangan kebijakan lebih lanjut untuk memastikan implementasi undang-undang yang efektif dan perlindungan data pribadi dalam domain IoT khususnya di Indonesia.
Maman Abdurohman and Marijn Janssen ,TU-Delft
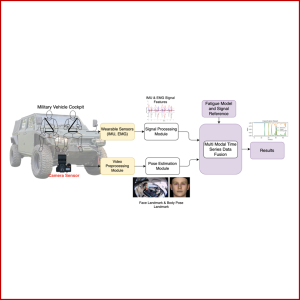
SENSOR FUSION
Kelelahan berkendara (fatigue driving) merupakan suatu significant concern, terutama pada kendaraan militer dimana keselamatan dan kinerja pengemudi sangat penting. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengembangkan system deteksi kelelahan berkendara (fatigue driving detection) menggunakan analisis biomekanik untuk pengemudi pada kendaraan militer seperti panzer. Dengan memantau sinyal biomekanik pengemudi, seperti postur, pengenalan kondisi mata dan wajah (facial landmark tracking), serta data dari vehicle vibration, tanda-tanda kelelahan dapat dideteksi dan memperingatkan pengemudi mengenai tingkat kelelahan mereka, sehingga meningkatkan kinerja serta keselamatan berkendara.
Bayu Erfianto and TNI AD
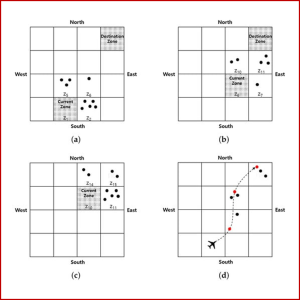
UAV SIMULATION AND OPERATING SYSTEM
Activities on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) have increased over the last years and there are many fields in which UAVs can be used. One of the basic applications is reconnaissance of a given area using multiple UAVs. To perform reconnaissance mission, there are two methods: (i) path planning to navigate the pre-determined route; and (ii) random mobility method to explore without prior knowledge. We indicate the imbalance problem of existing random mobility models for reconnaissance and propose a new model considering reconnaissance balance based on the number of visits. We divide the scanning area into N zones and then select a zone stochastically in which the search is insufficient.
M. Faris Fathoni and Gyeongsang National University, Korea
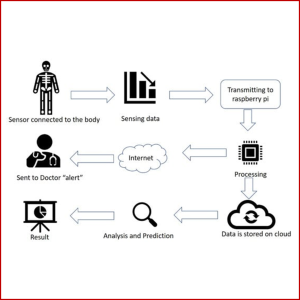
IoT FOR SAFETY DRIVING
This research presents a novel prototype applied in a real transportation system, particularly for buses, to avoid accidents, which may involve numerous victims, and even occasionally cause death. This system consists of a wearable device and embedded system with several sensors connected via Bluetooth, similar to the Internet of Things (IoT). Wearable devices are made to monitor the driver’s heart rate and alert the driver if they are in a state of sleep deprivation to prevent any potential accidents. The embedded system includes a Global Positioning System (GPS), accelerometers, and gyroscopes attached to a Smart Box mounted on the bus. The embedded system alert function will be triggered if an accident occurs and automatically sends the geolocation of the accident to the registered phone number through a message using a mobile phone.
M. Irsan and UMPSA, Malaysia
4. Penelitian Unggulan Kelompok Keahlian Software Engineering
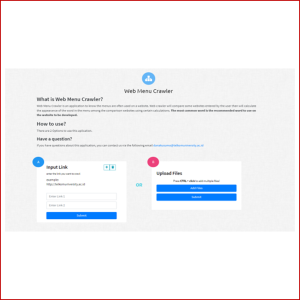
WEBSCOMPARE.COM
Bertujuan mengungkap menu-menu yang sering digunakan dalam pembuatan struktur web dengan membandingkan struktur menu sejumlah web melalui perhitungan kemunculan label menu melalui kalkulasi dengan basis jarak levenshtein.
Dana Sulistiyo Kusumo, Anisa Herdiani, Arief Luthdiyanto, Indra Lukmana Sardi, Kadek Aditya Cahayaputra, Shinta Yulia Puspitasari
SIABDes TAxion
SIABDes TAxion (Aplikasi Akuntansi BUMDes), sebuah kolaborasi Fak.Informatika dan Fak. Ekonomi dan Bisnis yang menstimulus digitalisasi pengelolaan keuangan BUMDes dan telah meraih juara pertama Kompetisi Inovasi Bandung BEDAS.
TEST CASES CATALOG APPS
Aplikasi yang merekonstruksi pengalaman pembuatan kasus-kasus pengujian perangkat lunak berdasarkan pengalaman empiris
Aqila Fitri Alitu, Rosa Reska Riskiana dan Dana Sulistiyo Kusumo
Alumni Engagement Apps
Pengembangan aplikasi untuk mengelola interaksi kampus dengan alumni melalui fitur: lowongan kerja, endowment (penggalangan dana alumni), dan penjajakan kemitraan. Aplikasi ini hasil kerja sama Fak.Informatika dan Bandung Techno Park.